Walesā biggest ever health infrastructure project, the Ā£350³¾ Grange University Hospital, was planned from the start for rapid delivery, using offsite methods and a collaborative approach ā but then covid-19 struck and the client needed beds available even faster. How did the project team do it?

Back in March when the coronavirus pandemic was just beginning to grip the UK, concerns around hospital capacity were emerging across the nation. In south-east Wales the need was immediate: for the Aneurin Bevan University Health Board, whose area then accounted for more than half of Walesā confirmed covid-19 cases, it was imperative to increase the number of available beds. The region was already home to Walesā biggest ever health infrastructure project, the Ā£350³¾ Grange University Hospital near Cwmbran, but that was not due to open for another 12 months.
As March drew to a close the hospital project team, led by architect BDP, project and cost manager Gleeds and main contractor Laing OāRourke, were approached by the health board to see if anything could be done to accelerate completion of the facility, which was being delivered using offsite and design for manufacture and assembly (DfMA).
They agreed to fast-track the build programme so that 350 new beds could be made available as soon as possible to coronavirus patients if required. On 27 April, just four weeks later, the health board took possession of 50% of the space within the hospital. This included most of the ward blocks and the ground floor of the diagnostic and treatment departments, as well as the pathology department, the pharmacy, FM services areas and the mortuary, as well as car parking zones and plant areas. NHS staff now have the ability to mobilise within three weeks to take patients at the new hospital if there is a second spike in covid infections.
In a webinar held as part of ŠŌ°ÉµēĢØās Proud to Help campaign, Laing OāRourke business unit leader Mike Lewis, Gleeds project director Victoria Head, BDP architect director Adrian Hitchcock and Nicola Prygodzicz, executive director of planning, digital and IT at the Aneurin Bevan University Health Board, shared how the use of offsite manufacturing on the project saved time, reduced the number of site workers and created a collaborative environment for solving problems.
Collaboration from the start
Prygodzicz said that when the Grange University Hospital was first conceived the trust was looking for an acute healthcare facility to provide the specialist care unavailable at local hospitals in the Gwent region. āIt took a year to get approval after the final business case was submitted. It couldnāt come quick enough for our clinical teams,ā said Prygodzicz, adding that a number of local hospitals were decommissioned during the time it took to deliver the project.
If we hadnāt had the foresight to use modern methods of construction we would not have been able to respond and help the health board
Victoria Head, Gleeds
Laing OāRourkeās Lewis described the clientās brief simply: āWe need this as quick as we can physically get it.ā The next step was setting up the project team, which along with Laing OāRourke, Gleeds and BDP included WSP and Aecom as engineering consultants and Arup as NEC supervisor. Having the design and construction teams both involved from a very early stage was essential as it enabled everyone to understand each otherās perspective, said Gleedsā Head.

According to Lewis, it was the use of the NEC suite of contracts that allowed this early collaboration and thereby facilitated the use of design for manufacture and assembly (DfMA). As Head said, this approach was integral to the projectās rapid delivery. āWe went into contract on a 137-week programme and we had to put in a lot of work to get partners there to say they were happy with that route,ā she said.
A traditional build would have taken 197 weeks rather than the 137 weeks of the DfMA route, she said ā a programme saving of 23%. āAny client is going to find that very compelling.ā
The design of the building was also approached with an eye to speed, as BDPās Hitchcock explained. āThe building is really about three quite distinct functional zones. The inpatient care zone is constructed as a ward block, and beds have been placed over beds [in the same positions on different floors] to simplify the engineering. The diagnostic and treatment zone is a very regular, simple block based on an 8:1 structural grid.
āIt was about trying to simplify the component parts of the building, so we developed a repetitive, simple structural grid form with adaptable ventilation and engineering services.ā
In excess of 50% of the project was delivered through Laing OāRourkeās various business arms, including structures and geotechnical specialist Expanded as well as Explore Manufacturing, which is central to Laing OāRourkeās DfMA approach. āWhen we do the next one we will be assembling even more, which will give us even greater pace and greater certainty,ā said Lewis.
MMC at Grange University Hospital
Offsite manufactured components used in the scheme include:
- 774 reconstituted stone, insulation and load-bearing inner-skin sandwich panels incorporating pre-installed windows
- 821 precast concrete columns
- 1,200 precast concrete shear walls
- 1,443 lattice planks
- 2,869 hollow-core pre-stressed planks used with 585 Peikko Delta beams
- 6 staircases precast throughout the five storeys of the building
- 243 bathroom pods manufactured from 3D models
- 661 horizontal corridor services modules
- 73 vertical services riser modules incorporating floors at each level
- 40 skid-mounted plant units
- 69 air-handling units, complete and pre-commissioned
Speeding up the programme
āIt was a Sunday afternoon when we received a text from Nicola [Prygodzicz] asking: can we talk tomorrow?ā said Head. Once Prygodzicz had put the trustās request for the accelerated programme to the team, they responded by reprioritising site activities and with a new commissioning strategy designed to allow for zonal access and reallocation of resources. The health board team were able to work alongside the project team on a live site, fitting out the wards with beds and equipment. This collaborative approach condensed the commissioning and soft landings periods from 12 weeks to four weeks.

Head said: āThe health board were reviewing the trajectories of how covid could hit Gwent, and we developed two plans to allow capacity in the system if required in the pandemic.ā Prygodzicz said that knowing how well progressed the hospital was it seemed a ānoābrainerā to ask the team if it was possible to make the 350 beds that might be needed to handle the pandemic available sooner, and that getting the revised plan approved in less than a week was a ārecord-breaker for the public sectorā.
Extensive resource planning was required, balancing the need to deliver a fast-track programme against ensuring the safety of the workforce, all of whom worked in line with government guidelines. āIt was an absolute priority to make sure this could be delivered safely,ā said Lewis.
All those who could work from home did so. On site, stringent hygiene measures were put in place along with patterns and methods of work that allowed for social distancing. Extended hours with split shifts were introduced, with the project team continuing work at weekends as well as over the Easter period to fulfil their commitment to the health board to deliver the hospital early.
There are lessons about how long some things take us to make decisions about in the public sector. Covid is making us reflect on the fact there are ways you can speed these up
Nicola Prygodzicz, Aneurin Bevan University Health Board
Of the costs of this acceleration, Head said: āOne of the things that are so very positive is that itās a long-term plan ā there hasnāt been an investment in something that will take be taken down. We have brought expenditure forward but not in an overinflated way.ā
According to Laing OāRourkeās Lewis, the use of NEC contracts has also kept costs down because they are real-cost contracts that must be agreed before expenditure can be made. āItās not like these field hospitals which are built at a premium and theyāve had to invest in it at pace,ā he said.
Lessons learned
The hospital is now on standby to operate as a fully functioning facility to support health services in south-east Wales in fighting the pandemic as and when infection data suggests it is necessary. Meanwhile, using careful segregation endorsed by infection control, building control and fire officers, work will continue on the remainder of the build with a view to formally completing the scheme this autumn ā six months earlier than planned.
āSitting here saying that fills me with a little bit of dread, but also a lot of passion,ā said Head. āIf we hadnāt had the foresight to use modern methods of construction we would not have been able to respond and help the health board.ā
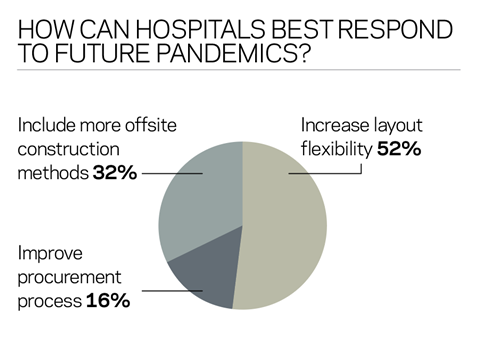
In terms of what can be learned from the project teamās experience, BDPās Hitchcock sees ramifications for hospital design. The Grange University Hospitalās arrangement of wards into groups of eight with a way in and way out to allow for one-way transit is something that could be carried forward onto other projects to help deal with potential future pandemics.
For Lewis, another takeaway is the need for shared platforms if the supply chain is to capitalise on the efficiency benefits of using DfMA: āBecause all our platforms were the same platforms, we were able to use the digital model as it was always intended. This has to be the way forward.ā Hitchcock agreed, saying BDPās ability to work directly with Expanded helped minimise error, highlighting the value of being able to freely share data.
So, can the public sector maintain the rapidity of decision-making seen on this project to help respond to the evolving covid-19 pandemic? Prygodzicz believes there are lessons to be learned here too. āWhile you canāt do everyday business with the level of [programme and cost] risk that we took, there are lessons about how long some things take us to make decisions about in the public sector,ā she said. āCovid is making us reflect on the fact there are ways you can speed some of these things up. There are a lot of lessons that can be learned around decision-making and governance for the public sector.ā
What the Grange University Hospital project shows perhaps most strikingly is the need to be more strategic around healthcare design and move away from highly bespoke products in hospital construction. If it can be done during a pandemic, then surely it can and should be done in the aftermath.
PROJECT SPECIFICS
Costs and programme
Ā£350³¾ out-turn cost
Ā£226³¾ construction cost
Ā£72³¾ M&E costs
137-week programme
Facilities
55,000³¾Ā² space
470 inpatient rooms
11 operating theatres
MRI scanner
Project team
Client Aneurin Bevan University Health Board
Architect BDP
Contractor Laing OāRourke
Project and cost manager Gleeds
Engineering team Aecom and WSP
NEC supervisor Arup
Tell us about the projects that make you proud to help
ŠŌ°ÉµēĢØ has launched its Proud to Help campaign to highlight the work construction is doing to support the countryās public services, critical works and supply chains, as well as setting it back on the road to recovery.
Contact us at newsdesk@building.co.uk with the subject line āProud to helpā or via LinkedIn or Twitter with your #ProudtoHelp stories
Downloads
Proud to help
Other, Size 5.35 mb






















No comments yet